第二回 AI(google tensorflow(テンソルフロー)の開発環境構築)PyCharmのインストール
tensotflow開発エディタPyCharmのインストール環境設定を行います。
第1章 PyCharmのインストールと設定
PyCharmのダウンロード
無償版のCommunityをダウンロードします。
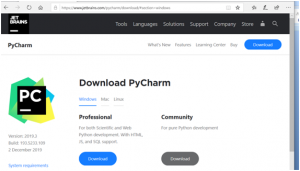
DOWNLOADを押すと、自動でインストーラがダウンロードされました。
(2) PyCharmのインストール
では、ダウンロードしたインストーラを起動しましょう。
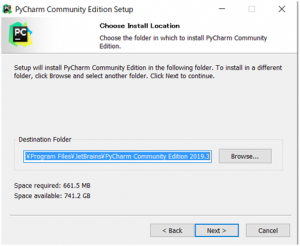
インストール場所は取りあえずデフォルトとしました。
全てにチェックを入れてください。
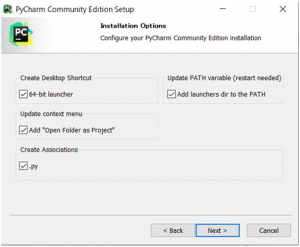
インストールが開始されます。
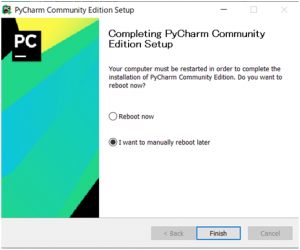
無事インストールが完了しました。
(3) PyCharmの起動と設定
早速PyCharmを起動すると以下のような画面が出ました。
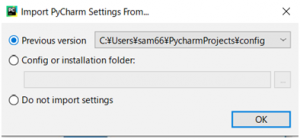
設定ファイルをインポートするか問われているようですが、使ったことないので取りあえずDo not import settingsです。
以下のカスタマイズはさしあたりはスキップでよいでしょう。
スタート画面に遷移します。早速「Create New Project」で新しいプロジェクトを作っていきましょう。
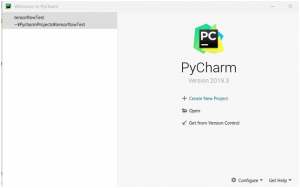
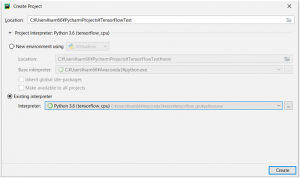
Project名は自由に決めてください。今回は「TensorFlowTest」としました。
「Existing interpreter」から、既に構築済の仮想環境のインタプリタを選択していきます。
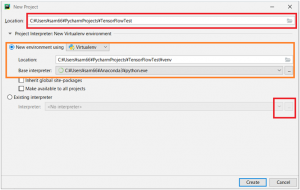
「Virtualenv Environment」で既に構築済の仮想環境のインタプリタを選択します。
Location::\Users\sam66\PycharmProjects\TensorFlowTest
●New environment using
Location: C:\Users\sam66\PycharmProjects\TensorFlowTest\env
Base interpreter: C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\python.exe
「Existing interpreter」より、右側の「…」を押して仮想環境を選択します。
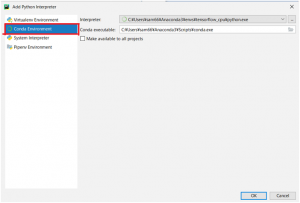
interpreter: C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\python.exe
Conda executable: C:\Usersam66\Anaconda3\Scripts\conda.exe
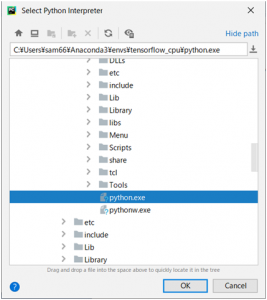
Anacondaのフォルダの「envs\仮想環境名\python.exe」を選択します。私の今回使用した仮想環境はtensorflow_cpuで、Tensorflowの環境構築を既に行っている仮想環境となります。
これで、インタプリタを選択できたのであとは「OK」で閉じます。
プロジェクトを「Create」しましょう。これでプロジェクトの作成は完了です。
(4) Tensorflowコードの実行
それでは、テストコードを実行してプロジェクトが実行できるか確認しましょう。
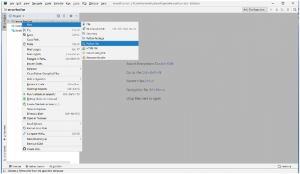
Project上で右クリックして、「New」→「Python File」で新しいファイルを作成します。
ファイル名は適当で大丈夫です。
作ったファイルに、コードを書きこみますが
tensorflow1.14.0 には、「TensorflowのMNIST For ML Beginnersに挑戦というサイトで作成されたものを使用します。
tensorflow2.0.0 には、低レベルAPIユーザーのためのTensorFlow2.0入門のソースコードを使用します。
●まずは、tensorflow2.0.0 のソースを実行してみたいと思います。
| import time import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf#========================================================================= # ネットワーク定義 #========================================================================= input_shape = (28, 28, 1) # 入力のshape. 最初の次元(バッチサイズ)は除く. # ネットワークの定義 # 入力層 x = tf.keras.layers.Input(input_shape) # 畳み込み層1 h = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding=‘SAME’)(x) h = tf.keras.layers.ReLU()(h) # 畳み込み層2 h = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding=‘SAME’)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.ReLU()(h) # 畳み込み層3 h = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding=‘SAME’)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.ReLU()(h) # 線形層 h = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()(h) y = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)(h)# モデルの作成 model = tf.keras.Model(x, y)#========================================================================= # 学習ステップの定義 #========================================================================= optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam(1.0e-4) train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean() # コスト記録用 train_acc = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy() # 精度計算・記録用 @tf.function def train_step(inputs): images, labels = inputs# tf.GtadientTapeブロックで入力からロスまで計算 with tf.GradientTape() as tape: logits = model(images) loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels, logits)# gradientを計算 # gradientを計算する重みをsourcesとして指定することが必須 # keras.Modelを使っているとmodel.trainable_variablesで渡すことができて便利 grad = tape.gradient(loss, sources=model.trainable_variables)# optimizerで重みを更新 optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grad, model.trainable_variables))# lossの値を記録 train_loss.update_state(loss) # train_loss(loss) # このように単純に__call__しても良い # 精度を記録 train_acc.update_state(labels, logits) # train_acc(labels, logits) # このように単純に__call__しても良い import time import numpy as np#========================================================================= # データセット #========================================================================= # データセットをロード # 今回はMNIST (X_train, Y_train), (X_test, Y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data() X_train = X_train[…, np.newaxis].astype(np.float32) Y_train = Y_train.astype(np.int32) N = X_train.shape[0]# tf.data.Dataset APIを使う batch_size = 32 dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X_train, Y_train)) dataset = dataset.shuffle(buffer_size=N) dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=True)#========================================================================= # Dataset APIで学習を実行 #========================================================================= print(‘train with Dataset API.’) epochs = 10 for images, labels in dataset: # 1step分のデータを取り出し train_step((images, labels)) # 1step分の学習を実行 # epochの結果を表示 time_epoch = time.time() – time_start # epoch毎にリセットしないと累積していく train_loss.reset_states() # 学習済みの重みを保存 model.save_weights(‘weights_{:}’.format(epochs)) #========================================================================= # numpy配列を直接与えて学習を実行 #========================================================================= epochs = 10 # ここから違う======================================================== # 1step分の学習を実行 # numpy配列を直接入れてOK train_step((images, labels)) # ここまで違う======================================================== # epochの結果を表示 time_epoch = time.time() – time_start # epoch毎にリセットしないと累積していく train_loss.reset_states() # 学習済みの重みを保存 model.save_weights(‘weights_{:}’.format(epochs)) |
ツールバーのRun -> testを実行すると下記の結果が表示されます。
| C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\python.exe C:/Users/sam66/PycharmProjects/TensorFlowTest/test1.py 2019-12-29 13:32:47.128485: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:142] Your CPU supports instructions that this TensorFlow binary was not compiled to use: AVX2 train with Dataset API. epoch: 1 loss: 0.2079 acc: 94.96% time: 464.62s epoch: 2 loss: 0.0433 acc: 98.69% time: 475.64s epoch: 3 loss: 0.0249 acc: 99.21% time: 542.55s epoch: 4 loss: 0.0163 acc: 99.43% time: 525.74s epoch: 5 loss: 0.0121 acc: 99.58% time: 510.17s epoch: 6 loss: 0.0078 acc: 99.75% time: 488.96s epoch: 7 loss: 0.0081 acc: 99.70% time: 485.95s epoch: 8 loss: 0.0055 acc: 99.80% time: 492.47s epoch: 9 loss: 0.0051 acc: 99.83% time: 488.59s epoch: 10 loss: 0.0037 acc: 99.88% time: 490.13s train with numpy array. epoch: 1 loss: 0.0029 acc: 99.90% time: 462.90s epoch: 2 loss: 0.0026 acc: 99.90% time: 459.85s epoch: 3 loss: 0.0038 acc: 99.88% time: 461.69s epoch: 4 loss: 0.0013 acc: 99.96% time: 462.34s epoch: 5 loss: 0.0015 acc: 99.95% time: 474.23s epoch: 6 loss: 0.0024 acc: 99.92% time: 464.11s epoch: 7 loss: 0.0029 acc: 99.91% time: 463.67s epoch: 8 loss: 0.0020 acc: 99.94% time: 471.60s epoch: 9 loss: 0.0011 acc: 99.96% time: 520.75s epoch: 10 loss: 0.0018 acc: 99.95% time: 518.38s |
上記の結果が出れば正常に処理されております。
次に、tensorflow1.14.0 のソースコード実行いたします。
その前に、tensorflow2.0.0をアンインストールして、tensorflow1.14.0をインストールします。
「juypyterlab」の「Terminal」から
pip uninstall tensorflow -y
pip uninstall tensorflow-estimator -y
pip uninstall tensorboard -y
anaconda3\enc\lib\site-pakage\配下に上記のディレクトリがあれば削除
pip install tensorflow==1.14.0
これで、tensorflow1.14.0がインストールされました。
PycharmのProject上で右クリックして、「New」→「Python File」で新しいファイルを作成します。
ファイル名にtest1として作成します。
| # from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import division from __future__ import print_functionfrom tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_dataimport tensorflow as tf# Mnistに使うデータセットをインポートする mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(“MNIST_data/”, one_hot=True) # グラフの作成 # 正解ラベル用のplaceholeder # 損失の計算方法と、オプティマイザーを定義 # セッションの作成と初期化 # 学習部(1000回学習) # テスト部 |
赤い部分は、WARNINGが出るため後継の関数に変えてあります。
いろいろWARNINGがでますが、
0.9189
Process finished with exit code 0
がでたら、正常終了です。
|
C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\python.exe C:/Users/sam66/PycharmProjects/TensorFlowTest/test.py C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\framework\dtypes.py:516: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_qint8 = np.dtype([(“qint8”, np.int8, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\framework\dtypes.py:517: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_quint8 = np.dtype([(“quint8”, np.uint8, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\framework\dtypes.py:518: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_qint16 = np.dtype([(“qint16”, np.int16, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\framework\dtypes.py:519: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_quint16 = np.dtype([(“quint16”, np.uint16, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\framework\dtypes.py:520: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_qint32 = np.dtype([(“qint32”, np.int32, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\framework\dtypes.py:525: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. np_resource = np.dtype([(“resource”, np.ubyte, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorboard\compat\tensorflow_stub\dtypes.py:541: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_qint8 = np.dtype([(“qint8”, np.int8, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorboard\compat\tensorflow_stub\dtypes.py:542: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_quint8 = np.dtype([(“quint8”, np.uint8, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorboard\compat\tensorflow_stub\dtypes.py:543: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_qint16 = np.dtype([(“qint16”, np.int16, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorboard\compat\tensorflow_stub\dtypes.py:544: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_quint16 = np.dtype([(“quint16”, np.uint16, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorboard\compat\tensorflow_stub\dtypes.py:545: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. _np_qint32 = np.dtype([(“qint32”, np.int32, 1)]) C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorboard\compat\tensorflow_stub\dtypes.py:550: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or ‘1type’ as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / ‘(1,)type’. np_resource = np.dtype([(“resource”, np.ubyte, 1)]) Extracting MNIST_data/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz WARNING:tensorflow:From C:/Users/sam66/PycharmProjects/TensorFlowTest/test.py:11: read_data_sets (from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Please use alternatives such as official/mnist/dataset.py from tensorflow/models. WARNING:tensorflow:From C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\learn\python\learn\datasets\mnist.py:260: maybe_download (from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.base) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Please write your own downloading logic. WARNING:tensorflow:From C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\learn\python\learn\datasets\mnist.py:262: extract_images (from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Please use tf.data to implement this functionality. WARNING:tensorflow:From C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\learn\python\learn\datasets\mnist.py:267: extract_labels (from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Please use tf.data to implement this functionality. WARNING:tensorflow:From C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\learn\python\learn\datasets\mnist.py:110: dense_to_one_hot (from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Please use tf.one_hot on tensors. Extracting MNIST_data/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz Extracting MNIST_data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz Extracting MNIST_data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz WARNING:tensorflow:From C:\Users\sam66\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow_cpu\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\contrib\learn\python\learn\datasets\mnist.py:290: DataSet.__init__ (from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Please use alternatives such as official/mnist/dataset.py from tensorflow/models. WARNING:tensorflow:From C:/Users/sam66/PycharmProjects/TensorFlowTest/test.py:25: softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits (from tensorflow.python.ops.nn_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Future major versions of TensorFlow will allow gradients to flow See `tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2`. 2019-12-29 17:40:40.072583: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:142] Your CPU supports instructions that this TensorFlow binary was not compiled to use: AVX2 Process finished with exit code 0 |
第三回は、tensorflow2.0.0のソースについて説明いたします。

